Topic: Human Female Reproductive System
Human Female Reproductive System
Some organs in the human body are represented in the diagram below.
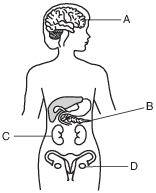
A sudden change in the DNA of cells developing in which organ could be passed to future generations?
(1) A
(2) B
(3) C
(4) D

Structure A usually produces
(1) sperm and eggs
(2) testosterone and eggs
(3) estrogen, progesterone, and eggs
(4) estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone
The diagram below represents one stage during the human reproductive process.

A function of structure A is to
(1) remove nutrients from the fetus
(2) provide the fetus with metabolic wastes
(3) remove all toxins from the blood of the mother
(4) provide for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Human reproduction usually involves
(1) internal fertilization and internal development
(2) external fertilization and external development
(3) internal fertilization and external development
(4) external fertilization and internal development
The diagram below represents a stage in the development of a fetus.

A major function of structure X is to
(1) produce gametes by meiosis
(2) protect the fetus from physical injury
(3) exchange materials between the mother and the fetus
(4) store food to provide the fetus with nutrients
The diagram below represents structures found in the female reproductive system.

If the areas labeled A were completely blocked on both sides, the most likely result would be that
(1) egg and estrogen production would stop
(2) sperm and insulin production would stop
(3) fertilization would not occur
(4) an embryo would develop
Which statement best describes an important process carried out by structure X?
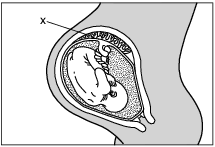
(1) Milk passes from the mother to the fetus.
(2) Materials are exchanged between fetal and maternal blood.
(3) Maternal blood is converted into fetal blood.
(4) Oxygen diffuses from fetal blood to maternal blood.
The major function of the placenta is to
(1) cushion the fetus so it won’t be hurt when the mother moves
(2) exchange food, oxygen, and waste between mother and fetus
(3) store food for the fetus
(4) support the egg for the process of fertilization
Occasionally, during pregnancy, the placenta can separate from the uterus. This causes a disruption in development and sometimes death of the fetus. Harm to the developing fetus might occur because the placenta
(1) transfers oxygen and nutrients to the fetal blood
(2) sends maternal blood into the fetus
(3) supplies milk for the fetus
(4) breaks down wastes of the fetus
Artificial Placenta
It is estimated that every year more than 15 million babies are born too early. The lungs of these premature infants are often immature and easily damaged. Premature births happen for a variety of reasons—some known and some unknown. Those that are known include infections and conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Scientists are researching what causes premature births, in an attempt to develop solutions to prevent them.
Scientists are also working on the development of an artificial placenta. At the University of Michigan, five premature lambs were placed in artificial placentas and kept alive for weeks. During this time, each lamb’s blood was circulated through its artificial placenta.
Discuss how the development of an artificial placenta is an important step in the study of premature births. In your answer, be sure to:
• explain why it would be harmful for a human mother’s blood to pass across the placenta and into the
fetus [1]
• state how an artificial placenta would be of benefit to the lungs of premature infants [1]
• explain why the lambs’ blood must be filtered as it circulates through the artificial placenta [1]
• state one reason why premature lambs were likely used as model organisms in this study rather than
mice [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 10 Allow 1 credit for stating why it would be harmful for a human mother’s blood to pass across the
• placenta and into the fetus. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The mother’s blood may be interpreted as a pathogen and attacked by the fetus’s immune
• system.
• — The mother’s blood could contain chemicals and pathogens that could harm the fetus.
• — It could cause an immune response.
• — It could be a different blood type that could cause a reaction.
• — It could harm the fetus’s organs.
• 11 Allow 1 credit for describing how an artificial placenta would be of benefit to the lungs of
• premature infants. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The lungs would be able to continue to mature, and the premature infant would not have
• to breathe on its own too soon.
• — The artificial placenta would perform the same processes as the natural placenta, allowing
• the lungs to continue to develop.
• — The artificial placenta would supply oxygen until lungs developed.
• — It would be of benefit because it prevents the accumulation of carbon dioxide.
• — It would help lessen complications associated with the mother’s high blood pressure/
• diabetes.
• 12 Allow 1 credit for explaining why the lambs’ blood must be filtered as it circulates through the
• artificial placenta. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The blood contains waste products that need to be removed.
• — Filtering removes wastes from the blood.
• 13 Allow 1 credit for discussing why premature lambs were likely used as model organisms in this
• study rather than mice. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Lambs are larger and more similar to human fetuses than mice are.
• — The development of a premature lamb is more similar to that of a human.
The Critical Role of the Placenta
The proper functioning of the placenta is critical to the growth and development of a healthy fetus. For example, the placenta appears to act as a nutrient sensor. It regulates the amounts and types of nutrients that are transported from the mother to the fetus.
Improper functioning of the placenta can alter the structure and function of specific cells and organ systems in the developing fetus, putting it at risk for health problems as an adult. For example, in some pregnancies, the placenta develops a resistance to blood flow. This resistance appears to force the heart of the fetus to work harder. This could result in an increased chance of the individual developing heart disease as an adult. A group of hormones known as glucocorticoids affects the development of all the tissues and organ systems. One of the things this group of hormones does is to alter cell function by changing the structure of cell membrane receptors.
Discuss the importance of the placenta in the development of a healthy fetus. In your answer, be sure to:
• identify two factors that could influence the nutrients that can pass from the mother to the fetus [1]
• identify the group of hormones that alter cell membrane receptors and explain how this alteration can affect cell function [1]
• state the role of the uterus in the development of the fetus and the placenta [1]
The student’s response to the bulleted items in the question need not appear in the following order.
• 14 Allow 1 credit for identifying two factors that could influence the nutrients that can pass from the mother to the fetus. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — diet of the mother
• — hormones
• — blood supply to the placenta
• — the ability of the placenta to sense nutrients
• — concentration of nutrients in the blood/blood vessels
• — permeability of the placenta
• — improper functioning of the placenta
• — illness/disease
• — size of molecules
• 15 Allow 1 credit for identifying the group of hormones that alter cell membrane receptors and for explaining how this alteration can affect cell function. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — Glucocorticoids–Receptors have a specific shape that determines their function. If the shape of a receptor is altered, it might not be able to perform its job appropriately.
• — Glucocorticoids–They alter cell function by changing the structure of the cell membrane receptors.
• — Glucocorticoids–They alter receptors to help them function.
• 16 Allow 1 credit for stating the role of the uterus in the development of the fetus and the placenta.
• Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The uterus is where the placenta forms and the fetus develops.
• — provides protection
Estrogen is one of the hormones produced by human females. Identify one organ that produces estrogen and state one specific function of estrogen in a human female. [1]
Organ:
Function:
Allow 1 credit for identifying the ovary/adrenal glands and stating one specific function of estro-
• gen in a human female. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — regulate the reproductive system
• — Estrogen affects the development of the sex organs/sex cells.
• — Estrogen plays a role in the menstrual cycle.
Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) are associated with some severe human diseases and are inherited through the cytoplasm in the egg cell. These diseases vary, but often affect organs and tissues with the highest energy requirements, including the brain, heart, muscle, pancreas, and kidney.
Scientists have successfully used mitochondrial replacement therapy with monkeys. Scientists are considering using this technique to reduce the incidence of mitochondrial disease in children. The proposed treatment would involve removing the nucleus from an egg donated by a healthy woman and replacing it with an egg nucleus from a patient (mother) with mitochondrial disease. This would place the patient’s egg nucleus into the cytoplasm of the donor’s egg containing healthy mitochondria. The egg is then fertilized with the father’s sperm externally using in vitro fertilization (IVF) to produce a zygote. The zygote is cultured for a few days to produce an embryo.
Explain what must be done with the embryo after in vitro fertilization (IVF) has been completed so the embryo can complete development. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — The embryo should be placed in the mother’s uterus.
• — To complete development, the embryo needs to be put into the mother’s uterus.
• — Implant it into the mother.
Cancer of the ovary is not common, but when it occurs, the cancer can cause the ovary to malfunction. Identify one possible result of an ovary not performing its intended function in the body. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — No eggs would be produced/sterility.
• — A female might not produce estrogen/progesterone.
• — An egg would not be released by the ovary.
• — A woman might have difficulty becoming pregnant.
• — Female characteristics would be influenced.
• — disrupts the female’s menstrual cycle
The diagram below represents the human female reproductive system.
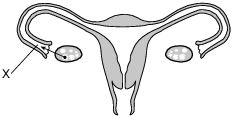
State one way a complete blockage at location X would affect the reproductive process. [1]
Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• — This will prevent the egg from reaching the uterus.
• — The egg will not be fertilized since sperm will be blocked.
• — This will prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
• — The other oviduct is not blocked, so fertilization could still occur.
• — The blockage will reduce the chance of a pregnancy.
